
It is critical to examine the urine anions to determine the compartment of origin of particles excreted with K and thereby whether hyponatremia will result in overall expansion or contraction of the ICF volume. In cell biology, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Hyponatremia is associated with cell swelling only if its cause is positive water balance and/or is loss of Na from the ECF.

In this model for acute hyponatremia, its basis was electrolyte loss, but the ECF volume was not contracted, suggesting that water shifted from the ICF to the ECF. Despite the negative balance for NaCl, the ECF volume as assessed by 3H-inulin space was not contracted. There were negative balances for Cl (2.4 ± 0.2 mmol) and phosphate (0.7 ± 0.05 mmol).
#INTRACELLULAR FLUID MANUAL#
From: Oh's Intensive Care Manual (Seventh Edition), 2014. Since these rats had a small negative balance for water (4 ± 1 ml), hyponatremia was due to their negative balances for Na (2.2 ± 0.3 mmol) and K (2.2 ± 0.1). ICF is defined as all the body water within cells and, unlike the ECF compartment, is an inhomogeneous, multicompartmental entity, with different pH and ionic compositions depending upon the organ or tissue being considered. The concentration of Na in plasma fell from 139 ± 1 m m to 120 ± 2 m m 24 hours after the infusion of hypotonic saline ( P < 0.01). ICF is defined as all the body water within cells and, unlike the ECF compartment, is an inhomogeneous, multicompartmental entity, with different pH and ionic. They received half-isotonic saline to expand their extracellular fluid (ECF) volume by 20% a long acting antidiuretic hormone (DDAVP) preparation was given to prevent the excretion of electrolyte-free water. intracellular fluid liquid contained inside the cell membranes extracellular fluid liquid containing proteins and electrolytes including the liquid in blood.

Normal saline is the IV fluid used alongside the administration of blood products. It is administered to correct extracellular fluid volume deficit because it remains within the ECF. Rats ( N = 10) were deprived of food and water for 24 hours. Normal saline is the isotonic solution of choice for expanding the extracellular fluid (ECF) volume because it does not enter the intracellular fluid (ICF). We evaluated the impact of a negative balance for sodium (Na) and potassium (K) salts on the intracellular fluid (ICF) volume, emphasizing the role of anions excreted with K. Hyponatremia is a common electrolyte abnormality that causes symptoms as a result of swelling of brain cells. Intracellular fluid is often referred to as cytosol when discussing cellular functions.
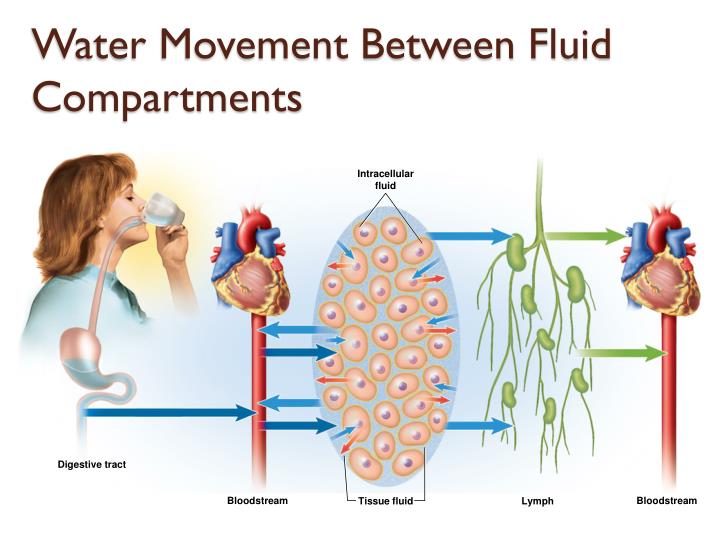
The interstitial fluid is a major component of the extracellular fluid. What is the impact of potassium excretion on the intracellular fluid volume: Importance of urine anions. Intracellular fluid is the fluid that exists within the cells of. The barrier that separates the interstitial fluid from the intracellular fluid is the plasma membrane.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
